Fingerprint Imaging Techniques – Using the DCS 5
From: Foster+Freeman
Posted On: 05 Nov 2024
Fingerprint imaging can prove be to a challenging process if you’re unsure of which techniques to use. Substrates, colour contrasting, light sources and filters leave fingerprint experts with an almost endless number of combinations when visualising a latent mark. Modern technology now allows examiners to achieve the best possible results under a variety of conditions. The Foster+Freeman DCS 5 is a comprehensive imaging system for the illumination, visualisation, photography, and enhancement of almost any type of fingerprint on any surface or background, ensuring that maximum detail is revealed.
5 Fingerprint Imaging Techniques to extract greater detail
Visible Contrast Imaging
Using multi-spectral illumination in the visible range to enhance the appearance of
fingermarks against a variety of backgrounds.
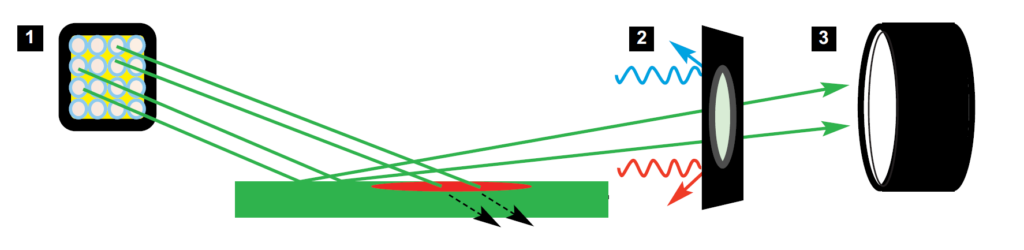
Technique
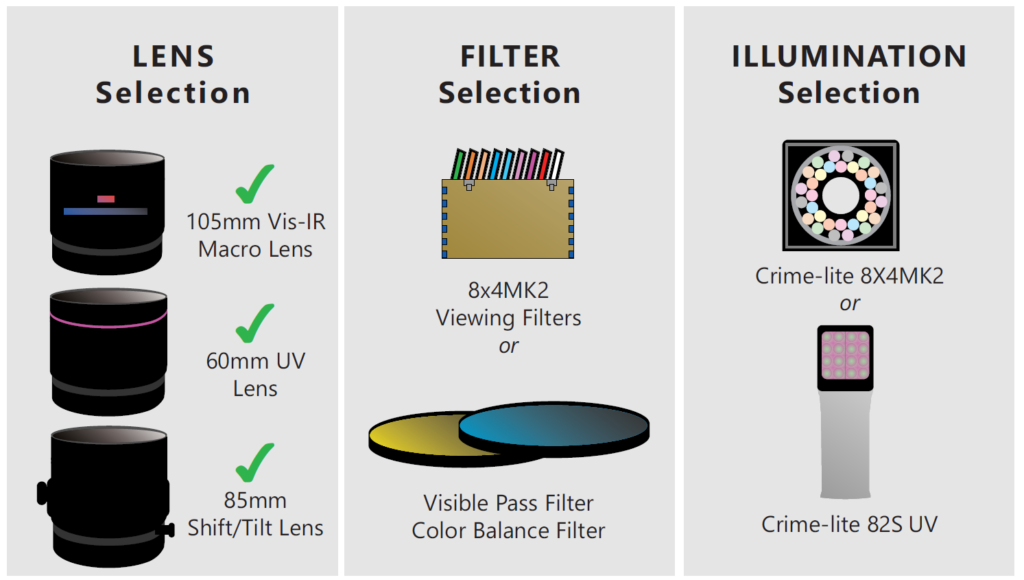
- Equip the camera with any DCS5 camera lens
- Attach a visible pass filter and colour balance filter (for colour correction)
- Illuminate evidence with a wavelength/colour that is opposite to the fingerprint (fingerprint treatment) but similar to the background substrate
*coloured glass filters may be attached to Halogen and FLS light guides* - Use a Crime-lite 8x4MK2 viewing filter to remove unwanted wavelengths
1 |
Illumination: |
Use any Visible light source |
2 |
Light Filtration: |
Use a Visible Pass and Colour Balance filter for colour correction |
3 |
Image Capture: |
Equip Camera with any DCS5 Lens article |
Applications
Visible contrast imaging enables the examiner to make a print more clearly visible
in cases where a coloured fingerprint appears on a coloured background.
- Colour filters can change the way we observe the subject
- Opposing colours intensify or darken each other
- Matching colours lighten themselves
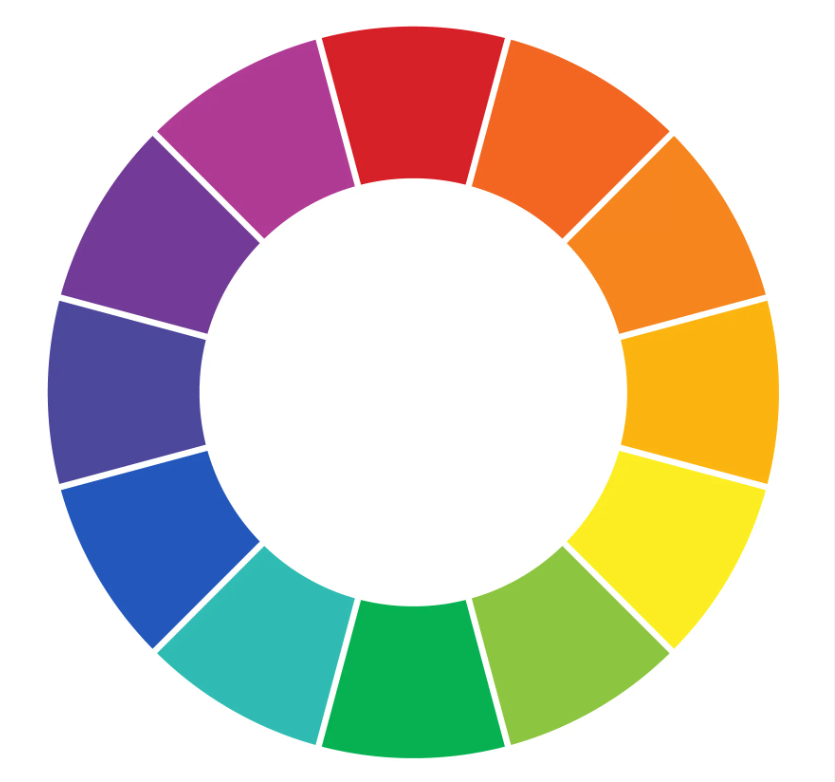

A traditional colour wheel can be used to discern opposing and
matching colours

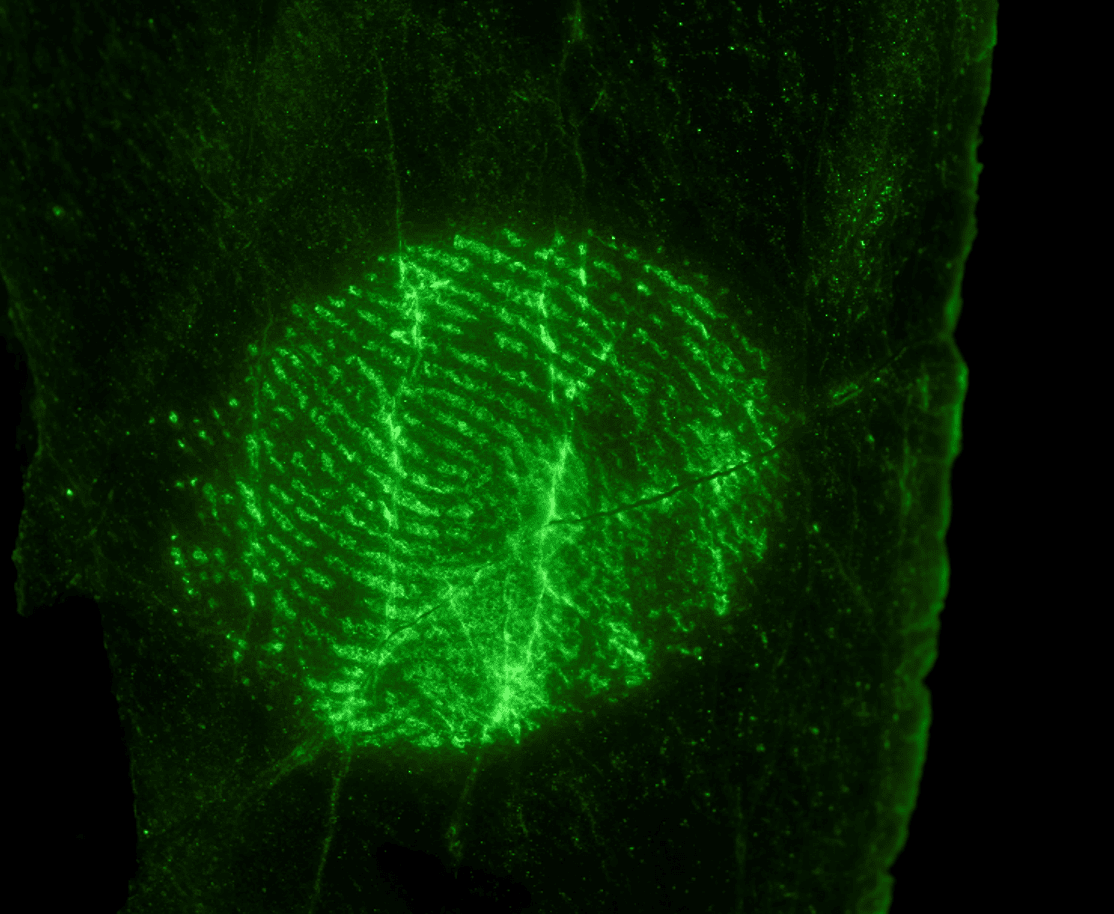
Using a green light to boost the contrast of fingerprints on newspaper treated with Ninhydrin
Reflected-UV
UV radiation (wavelengths of light shorter than 400nm) is invisible to the naked
eye. However, by equipping the DCS-5 camera with the 60mm UV Transmitting
Quartz Lens and 330-385nm bandpass filter, it is possible to record the UV
radiation that is reflected back from the subject to reveal impressive results from
previously difficult subjects.
Technique
- Equip the camera with 60mm UV transmitting lens & UV Pass Filter
*lock the lens on f45 to enable software control of the lens* - Illuminate evidence using the Crime-lite 82S UV or Crime-lite 8x4MK2
- Use DCS-5 Live View to view UV radiation and align evidence accordingly
*do not get too close – lens hotspots may occur at short working distances*
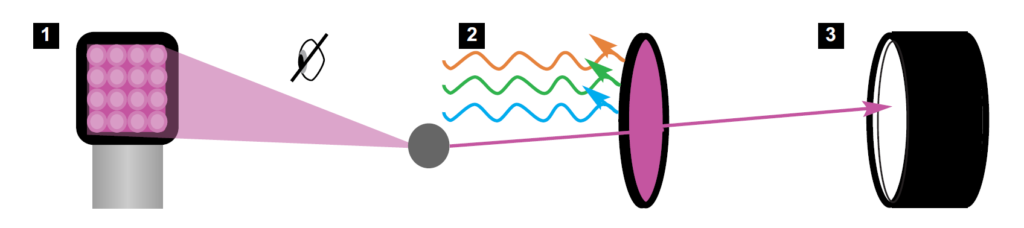
1 |
Illumination: |
Crime-lite 82S UV (365nm) or Crime-lite 8x4MK2 |
2 |
Light Filtration: |
330-385nm UV pass filter (blocks all visible light) |
3 |
Image Capture: |
60mm UV Transmitting Quartz Lens |
Applications
- Latent and cyanoacrylate (superglue) fumed marks
Both latent and fumed marks reflect UV to reveal sharp clear prints. - Glass and clear plastics
Transparent to the human eye, glass and most transparent plastics do not transmit UV so appear black when viewed in the UV waveband. - Pattern injuries, puncture wounds and bite marks
UV radiation does not penetrate deep into the skin meaning that surface wounds may be observed without being obscured by bruising. - Shoeprints, scuffs and tool marks
UV radiation scatters far more readily than visible wavebands of light allowing the examiner to better visualise surface marks and variations.
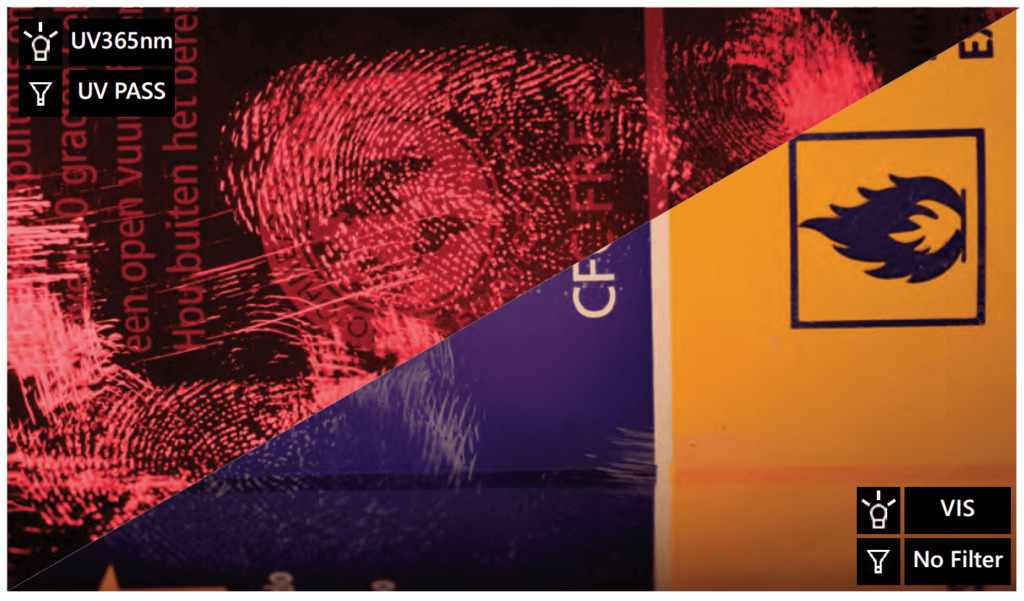

A fingerprint on a glass lightbulb, fumed with cyanoacrylate is visualised using reflected UV illumination

UV Fluorescence
Under intense UV radiation many substances, including body fluids, the natural secretions
of sweat present in latent fingerprint deposits, suspect fibres, and a number of commercial
fingerprint treatments, emit bright visible fluorescence.
Technique
- Equip the camera with the 105mm Macro Lens, 60mm UV Transmitting Lens, or the 85mm
Shift/Tilt lens - Attach the Visible Imaging Colour Balancing Filter to the lens
*for colour correction* - Attach the Visible Pass Filter to the lens
*to filter stray UV radiation* - Direct a UV light source (Crime-lite 8×4 or 82S UV) at the evidence
*fluorescence emitted in the UV waveband will now be visible*
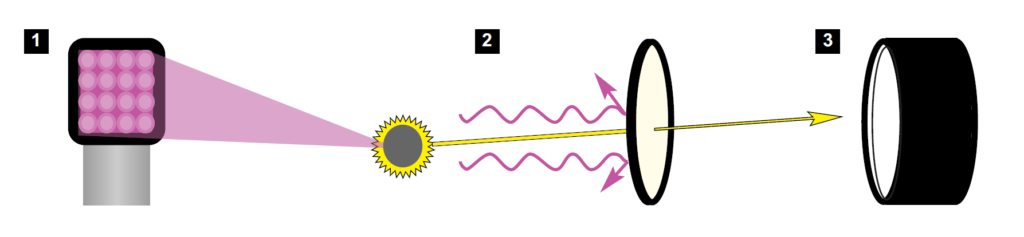
1 |
Illumination: |
Crime-lite 82S UV or Crime-lite 8×4 (365nm) |
2 |
Light Filtration: |
Visible pass filter (blocks stray UV radiation) |
3 |
Image Capture: |
105mm Macro or 60mm UV Transmitting Quartz Lens |
Applications
- Body Fluids, including saliva, semen, sweat, urine, vaginal secretions
UV radiation is widely used to exploit the natural fluorescent properties in body fluids. - UV fluorescent fingerprint treatments
PolyCyano UV, Ardrox, and some fluorescent powders have been designed specifically
for use with a UV light source. - Suspect fibres, and other items of trace evidence
Due to the countless variations in material, manufacturing process, dyes etc. fibres can
be caused to fluoresce under varying wavelengths including UV.
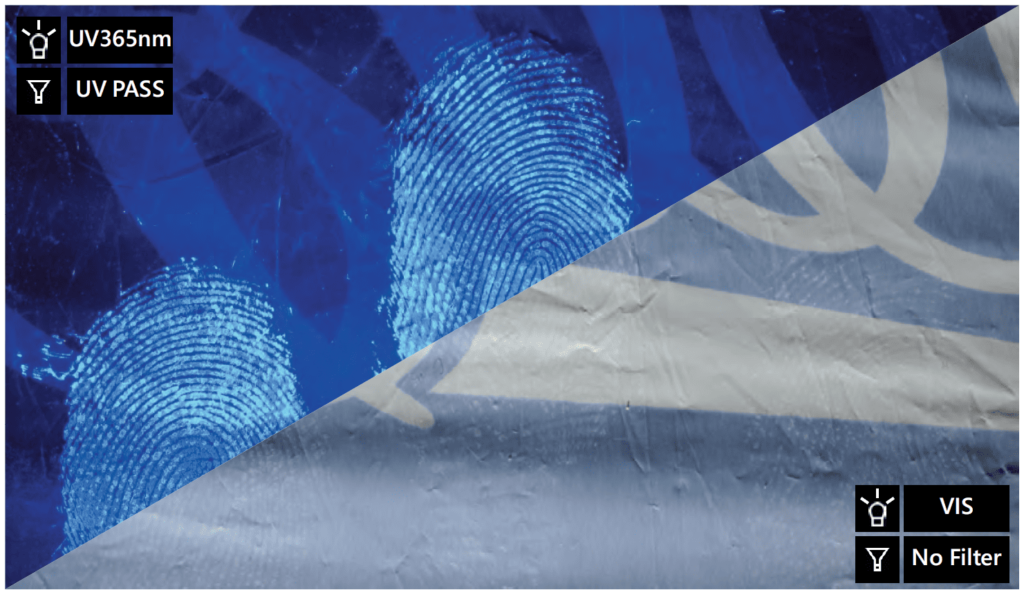

Fingerprints on a white plastic shopping bag fumed with PolyCyano and viewed under UV
NIR Fluorescence
Foster+Freeman’s new fpNATURAL range of fingerprint powders emit bright
Near-Infrared (NIR) fluorescence when illuminated with the appropriate
excitation waveband.
Technique
- Dust the evidence with fpNATURAL 1 or 2 powder
- Equip the camera with a lens & IR imaging filter
for fpNATURAL1 use the Crime-lite 8x4MK4 715nm or 780nm Viewing Filter
for fpNATURAL2 use the Crime-lite 8x4MK4 850nm or 900nm sharp-cut filter - Illuminate evidence using the Crime-lite 82S IR780 or Crime-lite 8x4MK4
for fpNATURAL1 use Red or Blue illumination
for fpNATURAL2 use 780nm NIR illumination - Use DCS-5 Live View to view IR fluorescence and align evidence accordingly
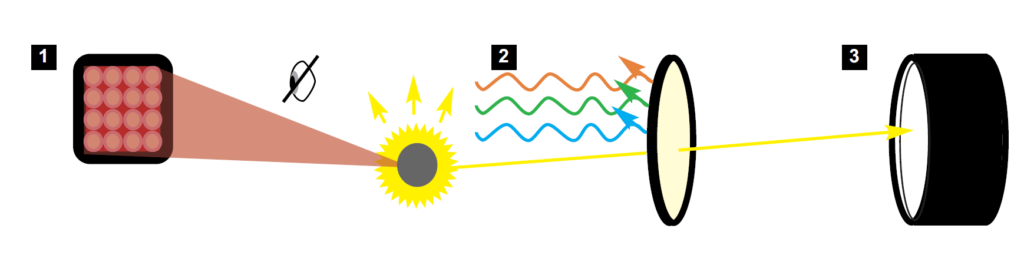
1 |
Illumination: |
Crime-lite 82S IR780 or Crime-lite 8x4MK4 |
2 |
Light Filtration: |
Crime-lite 8x4MK4 Viewing Filters |
3 |
Image Capture: |
Equip Camera with any DCS5 Lens |
Applications
fpNATURAL powders are highly effective at revealing high contrast NIR fluorescent fingerprints on the following evidence types:
- Paper and Polymer Banknotes
Viewed in the NIR, the complex backgrounds found on many banknotes is greatly suppressed - Colourful and/or patterned surfaces
Bright and colourful patterns can be seen to ‘drop out’ in the NIR - Cyanoacrylate fumed evidence
fpNATURAL powders adheres well to evidence that has been fumed with superglue

Fingerprints on a polymer banknote can be seen to fluoresce brightly under NIR illumination
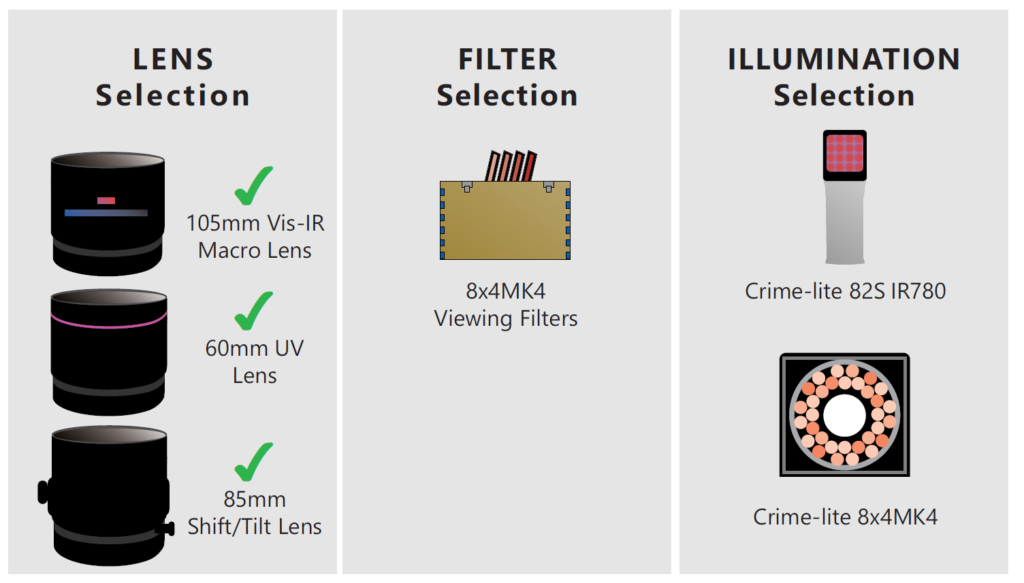
IR Reflection & Absorption
Differing substrates may absorb (appear to darken) or reflect (appear to lighten)
infrared illumination creating contrast between fingerprint and background
when viewed in the IR waveband.
Technique
- Equip the camera with any DCS5 camera lens
- Direct an IR light source at the evidence
- Filter the light entering the camera using an IR camera filter or a Crime-lite 8x4MK4 viewing filter
*contrast between IR reflective and IR absorbent materials may now be seen*
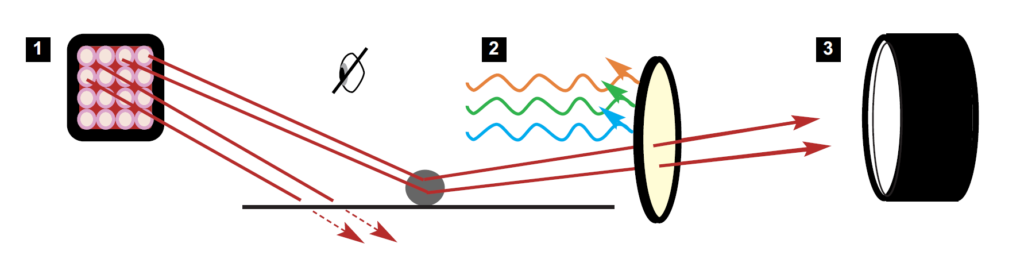
1 |
Illumination: |
Crime-lite 82S IR780, Halogen or FLS Forensic Light Source |
2 |
Light Filtration: |
Exclude UV and Visible wavelengths using an IR pass filter |
3 |
Image Capture: |
Equip Camera with any DCS5 Lens |
Applications
Broadly speaking, organic materials will absorb IR while synthetic materials are more likely to reflect.
- The following substrates may be expected to absorb IR
Organic fabrics (cotton etc.), wood, building materials including brick, stone and concrete, blood, gunshot residue. - The following substrates may be expected to reflect IR
Plastic wrappers, glossy paper, most metals, synthetic fibres, plants and foliage, glass and some plastics (plexiglass etc.)

Fingerprints dusted with black powder are revealed as the coloured background is suppressed
Need a quote or specs?
FIND OUT MORE
